Recent Emotet activity
Introduction
So far in 2018, I've seen a great deal of malicious spam (malspam) pushing Emotet malware. It's probably the most common malspam threat I've seen so far in 2018. Within the past week, the some good posts about Emotet have been published:
- 2018-07-18 - Symantec: The Evolution of Emotet: From Banking Trojan to Threat Distributor
- 2018-07-18 - Palo Alto Networks: Malware Team Up: Malspam Pushing Emotet + Trickbot
- 2018-07-20 - US-CERT: Alert (TA18-201A) Emotet Malware
- 2018-07-23 - MalFind: Deobfuscating Emotet’s powershell payload
You can also find indicators about Emotet by searching Twitter for #Emotet. Assuming you can wade through the re-posts on the above articles, you'll find a community that tweets indicators about Emotet like URLs for the initial Word document, file hashes for the malware, etc.
Emotet infection from Monday 2018-07-23
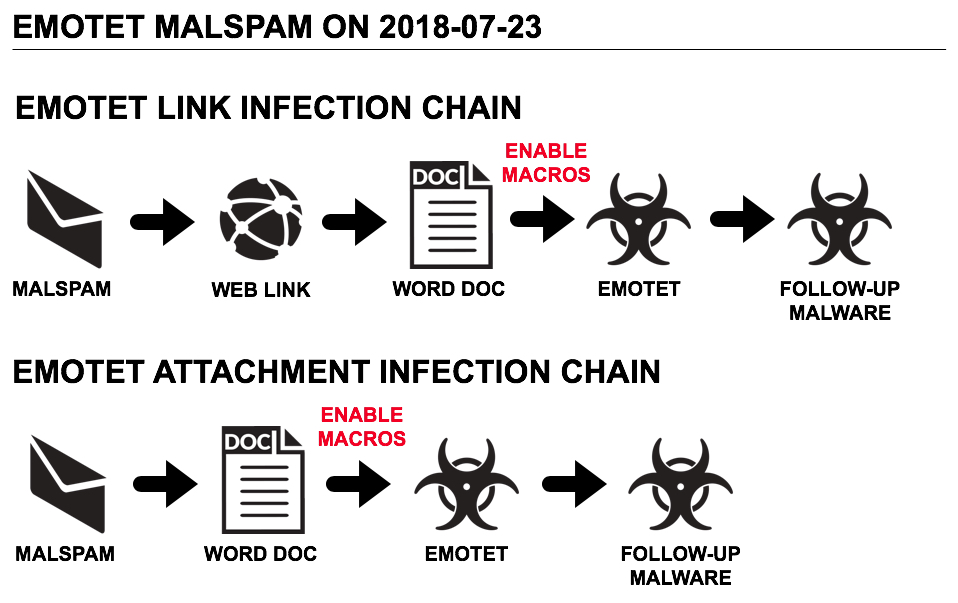
Shown above: Two different chain of events for Monday's Emotet infections.
On Monday 2018-07-23, I generated some Emotet infection traffic in my home lab, and I saw plenty of indicators. The following is malware retrieved from my infected Windows host:
- SHA256 hash: 9914881d35a7fa7ce6f9ec06d4e5c19f12c6916a57fcc4facbb28f144e921283
- File description: Downloaded Word doc with malicious macro that installs Emotet
- SHA256 hash: 83d54beb3fdecfc7bcb0eb048aa4634a5e4208dc0a3067a35d2cfb4598cb99b2
- File description: Emotet malware binary retrieved by Word macro
- SHA256 hash: b1ebf3d44d496ee574831266474b10b55c06e30aea56d41ac8830ba2b28f7a0f
- File description: Zeus Panda Banker
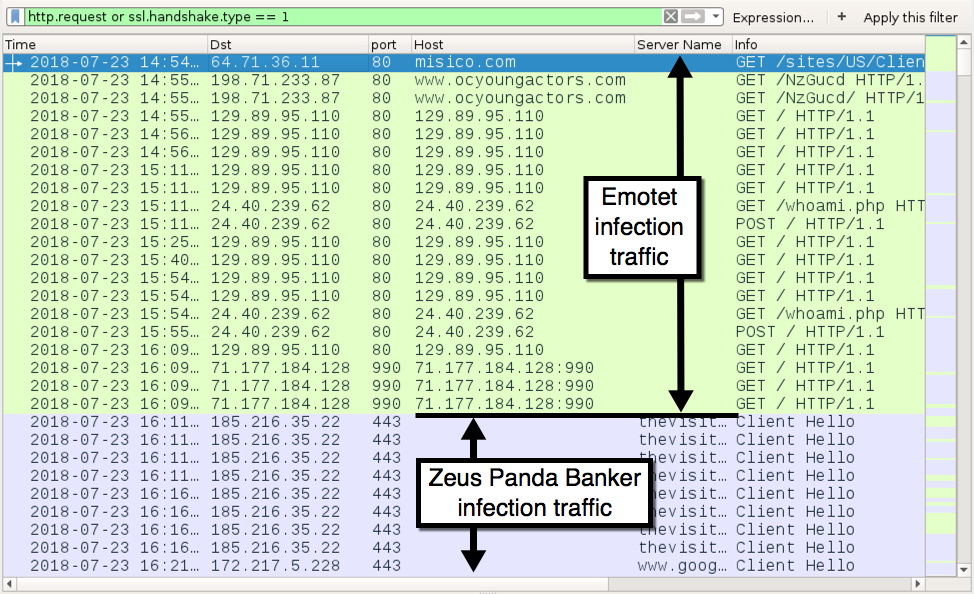
Shown above: Traffic from my infected Windows host filtered in Wireshark.
The following are domains, IP addresses, and URLs from the infection traffic.
Initial infection traffic:
- 64.71.36.11 port 80 - misico.com - GET /sites/US/Client/Invoice-0361376097-07-23-2018/
- 198.71.233.87 port 80 - www.ocyoungactors.com - GET /NzGucd/
Emotet post-infection traffic:
- 24.40.239.62 port 80 - 24.40.239.62 - GET /whoami.php
- 24.40.239.62 port 80 - 24.40.239.62 - POST /
- 46.105.131.69 port 8080 - 46.105.131.69:8080 - GET /
- 47.201.208.154 port 443 - 47.201.208.154:443 - GET /
- 70.183.113.54 port 8443 - 70.183.113.54:8443 - GET /
- 71.8.1.188 port 80 - 71.8.1.188 - GET /
- 71.71.3.84 port 80 - 71.71.3.84 - GET /
- 71.165.252.144 port 990 - 71.165.252.144:990 - GET /
- 71.177.184.128 port 990 - 71.177.184.128:990 - GET /
- 71.244.60.231 port 4143 - 71.244.60.231:4143 - GET /
- 73.27.38.128 port 80 - 73.27.38.128 - GET /
- 73.178.169.180 port 80 - 73.178.169.180 - GET /
- 79.78.160.225 port 80 - 79.78.160.225 - GET /
- 96.95.159.237 port 80 - 96.95.159.237 - GET /
- 96.95.159.237 port 8080 - 96.95.159.237:8080 - GET /
- 108.170.54.171 port 8080 - 108.170.54.171:8080 - GET /
- 118.244.214.210 port 443 - 118.244.214.210:443 - GET /
- 129.89.95.110 port 80 - 129.89.95.110 - GET /
- 129.89.95.241 port 80 - 129.89.95.241 - GET /
- 149.62.173.247 port 8080 - 149.62.173.247:8080 - GET /
- 186.85.246.153 port 8080 - 186.85.246.153:8080 - GET /
- 190.147.41.94 port 443 - 190.147.41.94:443 - GET /
- 199.120.92.245 port 80 - 199.120.92.245 - GET /
- 216.21.168.27 port 443 - 216.21.168.27:443 - GET /
Attempted TCP connections from Emotet infection, but no response from the server:
- 12.238.114.130 port 80
- 27.50.89.209 port 8080
- 46.105.131.87 port 80
- 47.150.11.161 port 7080
- 50.92.101.60 port 465
- 71.214.17.130 port 443
- 73.183.145.218 port 8443
- 78.47.182.42 port 8080
- 80.11.163.139 port 8080
- 108.246.196.73 port 80
- 118.190.60.27 port 20
- 146.185.170.222 port 8080
- 157.7.164.23 port 8080
- 192.42.116.41 port 443
- 194.88.246.242 port 443
- 194.150.118.8 port 443
- 199.119.78.9 port 443
- 199.119.78.38 port 443
- 222.214.218.192 port 4143
Zeus Panda Banker traffic:
- 185.216.35.22 port 443 - thevisitorsfilm.top - SSL/TLS traffic
Final words
As usual, properly-administered and up-to-date Windows hosts are not likely to get infected. System administrators and the technically inclined can also implement best practices like Software Restriction Policies (SRP) or AppLocker to prevent these types of infections.
A pcap of the infection traffic for today's diary can be found here.
---
Brad Duncan
brad [at] malware-traffic-analysis.net



Comments
Anonymous
Jul 24th 2018
6 years ago
https://urlhaus.abuse.ch/browse/tag/emotet
Most of the guys on Twitter have an API to this tool.
Cheers
PO3T
Anonymous
Jul 27th 2018
6 years ago