Malspam with password-protected Word documents
Introduction
On Monday 2017-03-20, the ISC received a notification through our contact page. Someone reported numerous items of malicious spam (malspam) sent to addresses at his organization. The malspam had Microsoft Word documents (.docx files) as attachments and subject lines such as:
- Fwd:Ticket k29y729n71c52h692o53171
- ReTicket 985v49f155t06g78v412a3n382
- Fwd:Ticket 048f1v00u98
- ReTicket y18k9178280
- Ticket p574v892f453b467
- Ticket e26099p58v65x073
- ReInquiry 9l48o77
- Inquiry m70q200kd80
- ReInquiry t63j288d271f997b083a57c547
- ReInquiry f514f830p417n06h5150s036r838
An example of the message text:
Check the payment report created for [recipient's email address] as you just ordered.
You may need Doc Passcode: [string of alphanumeric characters]
[fake sender's name]
The attached Word documents were approximately 70 kB in size and password-protected. The document file names started with the string of alphanumeric characters from the subject line followed by the recipient's email address. File names all ended with the .docx file extension.
This diary documents my investigation into this wave of malspam. We're always thankful for people who submit samples of emails and malware like this to the ISC.
The email
The email appeared somewhat common for most malspam we see. People sometimes think if malsapm has the recipient's name in the email, it must be targeted. However, that's often not the case. This type of malspam is easily automated, and it can seem convincing when the recipient's email address is formatted as [email protected].
.jpg)
Shown above: An example of the malspam.
The attachment
The document would only open after using the password from malspam it was attached to. This tactic typically allows the document to bypass detection in anti-virus tools. Searching VirusTotal for the Word document showed 0 of 56 detections when I checked the file later that day.
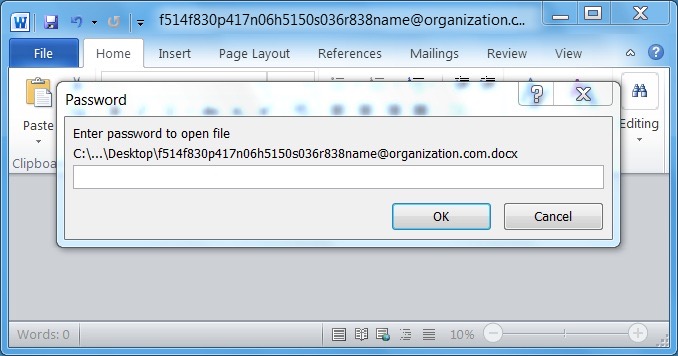
Shown above: Request for the attached document's password.
The document had three embedded objects that were supposedly Word documents. Dragging and dropping the objects onto the desktop revealed these were the same Visual Basic Script (VBS) file. The file name had several spaces before the .vbs file extension in an attempt to hide the true nature of the file.
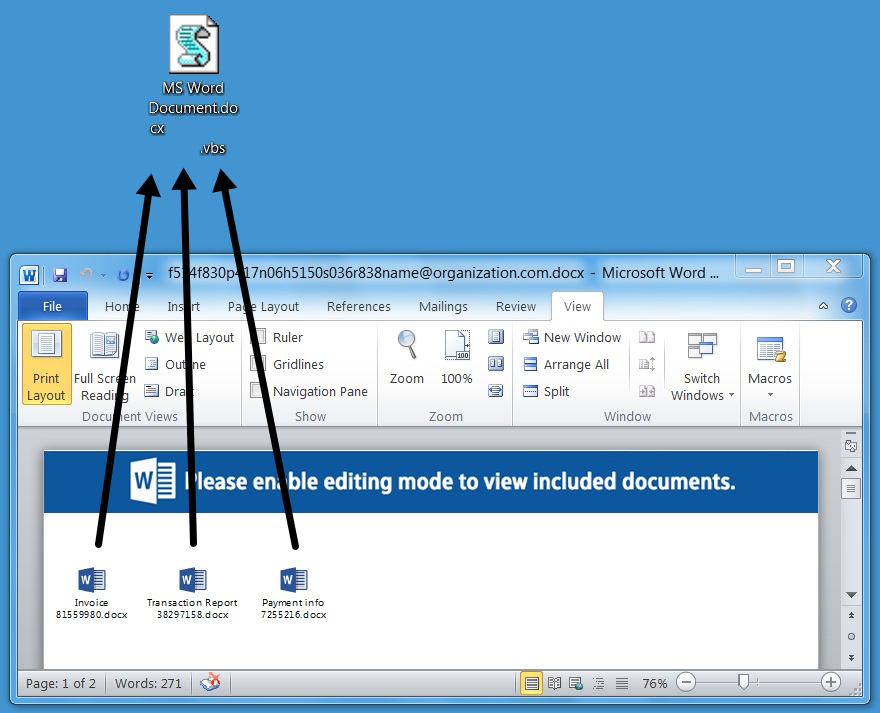
Shown above: The embedded objects were a VBS file.
The VBS script was obfuscated, so its purpose was not immediately apparent.
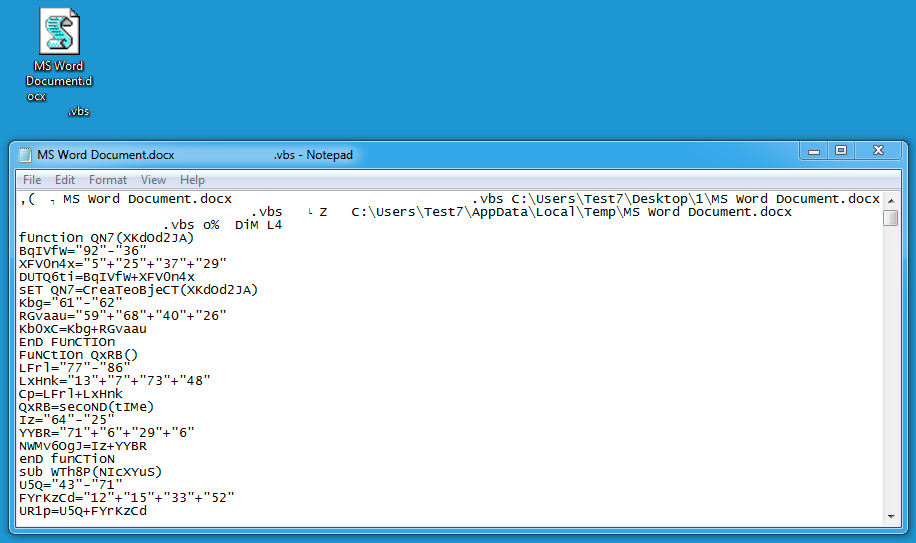
Shown above: Text from the embedded VBS file.
The traffic
Executing the VBS file on a Windows host in my lab generated HTTP traffic. This is typically an attempt to download additional malware like a Windows executable or DLL file. Unfortunately, by the time I checked it, the URL returned a 404 Not Found error.
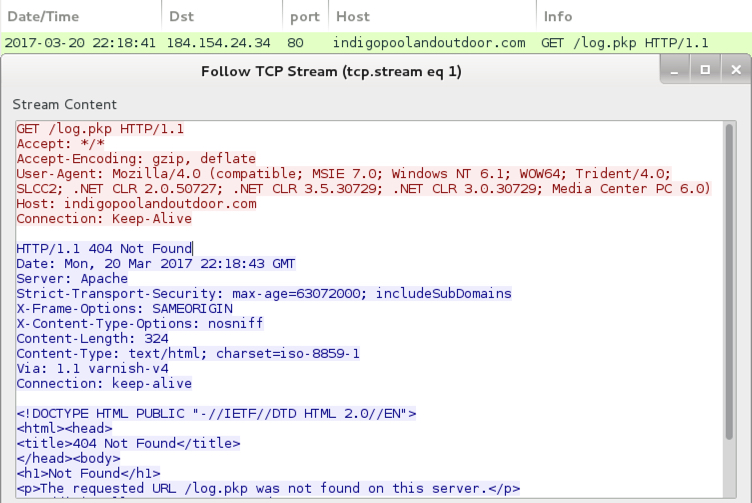
Shown above: Traffic generated by the .vbs file.
I searched reverse.it (also available as Payload Security on hybrid-analysis.com) and found 21 items submitted on Monday 2017-03-20 associated with the domain. Most were other documents from the same type of malspam. Two were attempts to analyze an extracted .vbs file. One was a query to the callback URL. None of these examples made it any farther than I did.
NOTE: Getting these search results on reverse.it requires a login. The accounts are free and only require a name, email, and password.
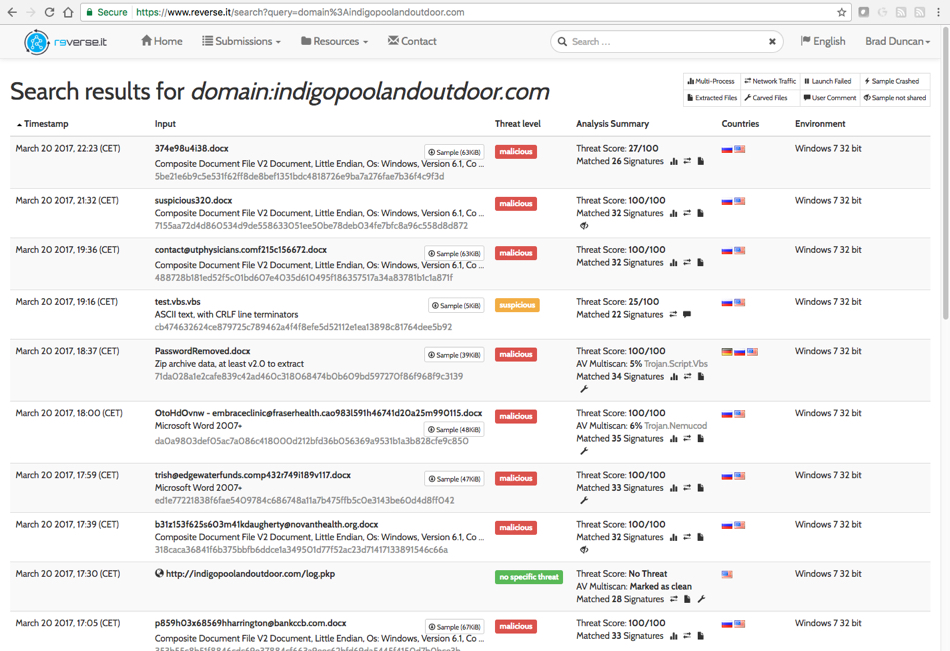
Shown above: Search results on reverse.it (hybrid-analysis.com) for the callback domain.
Indicators of compromise (IoC)
The following indicators are associated with today's malspam example:
Password-protected Word document:
- SHA256 hash: 146772487e4f4453055f80f40039ad1ce6c82a32a94d82a8c5bd228f4bcb4dcc
- File size: 70,656 bytes
- File name: f514f830p417n06h5150s036r838[recipient's email address].docx
Word document with password-protection removed:
- SHA256 hash: 2792084dcd04a51bde167afb59a912a5ae82adb33720fb0f25a10be9d08d2e12
- File size: 64,938 bytes
VBS file embedded in the Word document:
- SHA256 hash: 4cc6e847ada0ebe30d88d93b07c58024380626295d43135ca161473d0cd20cb9
- File size: 9,583 bytes
- File name: MS Word Document.docx .vbs
Traffic generated by the VBS file:
- 184.154.24.34 port 80 - indigopoolandoutdoor.com - GET /log.pkp
Final words
Last week, someone at cysinfo.com blogged about similar malspam designed to infect Windows hosts with an Ursnif banking Trojan. This type of password-protection technique in malspam attachments is nothing new. I've certainly seen it before, and some creative Google searching will reveal this started years ago. However, I haven't seen much about this in public forums lately.
Most security professionals assume we all know about it, so it doesn't usually make any headlines. I advise people this is still a thing.
Of course, properly-administered Windows hosts are far less vulnerable to this type of infection. The hosts I use in my lab environment are a different story. If anyone knows of someone who was actually infected from one of these password-protected documents, please share your tale in the comments.
---
Brad Duncan
brad [at] malware-traffic-analysis.net


Comments