Update: VBA Maldoc & UTF7 (APT-C-35)
In diary entry "VBA Maldoc & UTF7 (APT-C-35)", I analyze a malicious document with VBA code that injects shellcode into the host process. That shellcode is UTF7 encoded.
I did the UTF7 decoding with Python, but that resulted in an error. Still, I instructed Python to ignore that error, and I was able to recover a URL, but it was a bit corrupted (HTTP protocol):
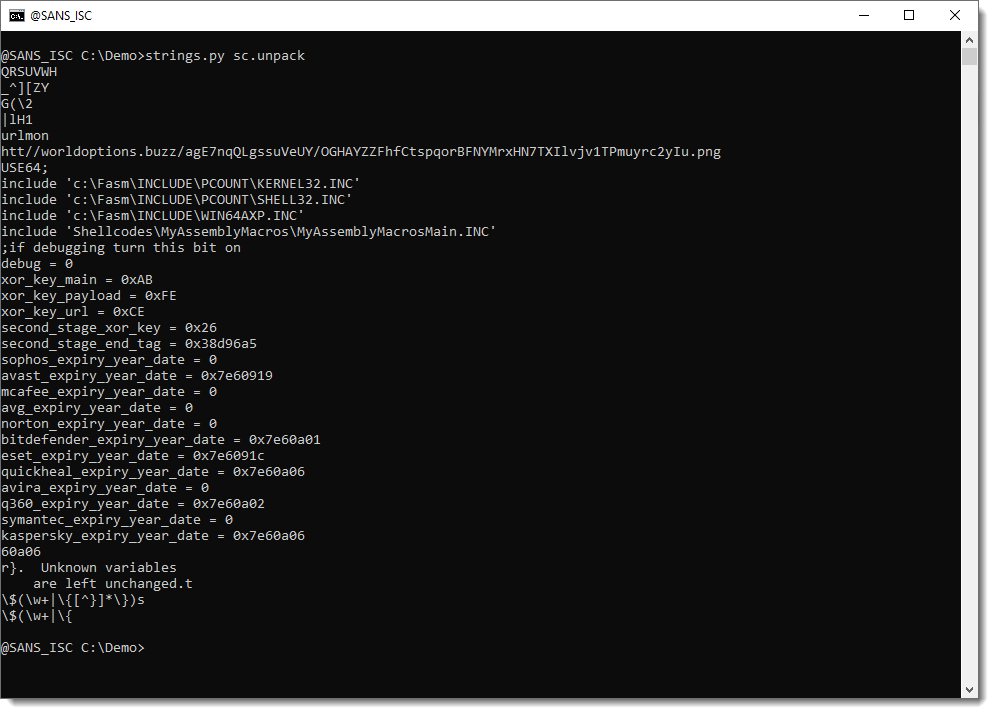
As can be seen, the decoded URL starts with htt//
I took a second look this weekend at this sample, and this time, I used WIN32 API function MultiByteToWideChar (from Python), just like the VBA code does.
I wrote a small decoding function for translate.py:
from ctypes import *
def DecodeUTF7(data):
result = bytes(10000)
windll.kernel32.MultiByteToWideChar(65000, 0, data, len(data), result, len(result))
return result
And then I used this to decode the UTF7 payload. And this time, I deobfuscated the decoded shellcode & strings with xorsearch.
This approach worked, both for the 32-bit and 64-bit shellcode:
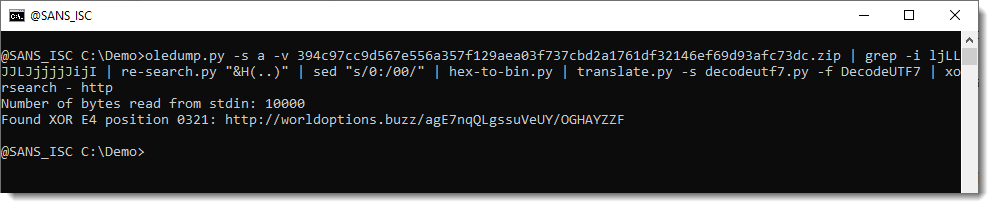
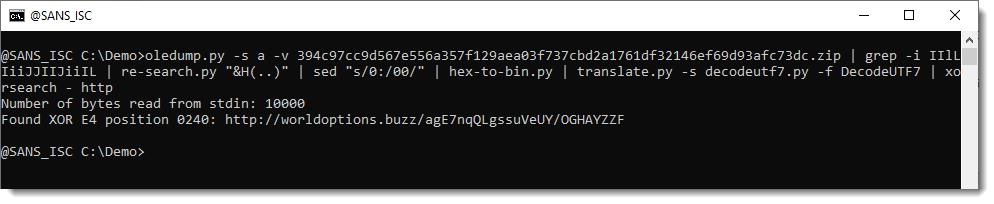
This approach (calling WIN32 API from Python) only works on Windows machines.
And you have to be careful not to execute malicious code accidentaly. Here I call a decoding function (MultiByteToWideChar), but if I would call another function that is used in the VBA code (Internal_EnumUILanguages), I would actually execute the shellcode.
Didier Stevens
Senior handler
Microsoft MVP
blog.DidierStevens.com


Comments