Fake Updates campaign still active in 2019
Introduction
Last week on 2019-02-06, @baberpervez2 tweeted about a compromised website used by the Fake Updates campaign (link to tweet). The Fake Updates campaign uses compromised websites that generate traffic to a fake update page. The type of fake update page depends on your web browser. Victims would see a fake Flash update page when using Internet Explorer, a fake Chrome update page when using Google Chrome, or a fake Firefox update page when using Firefox. Victims download JavaScript (.js) files from these pages disguised as browser updates. The downloaded .js files will instead install malware on a vulnerable Windows host.
Patterns for infection traffic are relatively unchanged since this campaign was first reported on the Malwarebytes blog in April 2018.
I generated an infection from the Fake Updates campaign on Friday 2019-02-09 and again on Monday 2019-02-11. Both times, the final payload was a Chthonic banking Trojan. Today's diary reviews the infection I generated on Monday 2019-02-11.
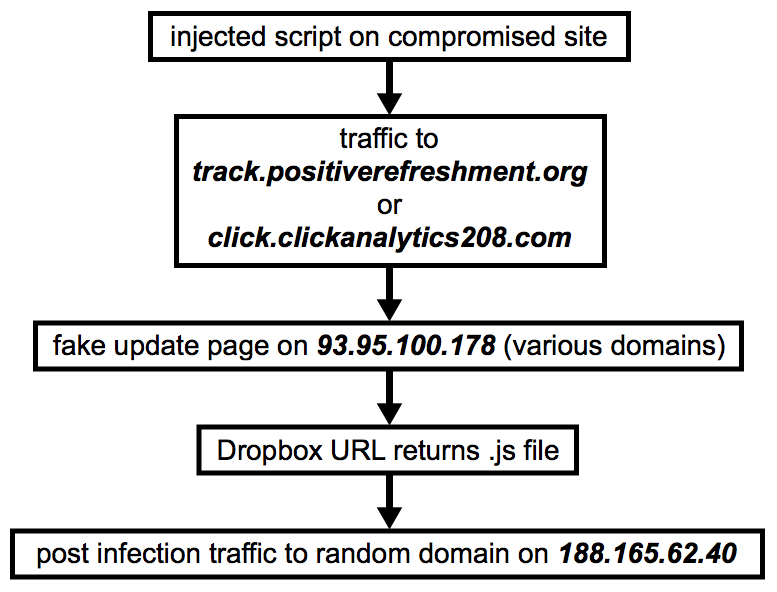
Shown above: Flow chart for infection traffic from Monday 2019-02-11.
Screenshots
The following ar screenshots on Fake Updates campaign traffic I generated from the inital compromised website at thetechhaus[.]com.

Shown above: Fake Chrome update page seen when thetechhaus[.]com was viewed in the Chrome web browser.
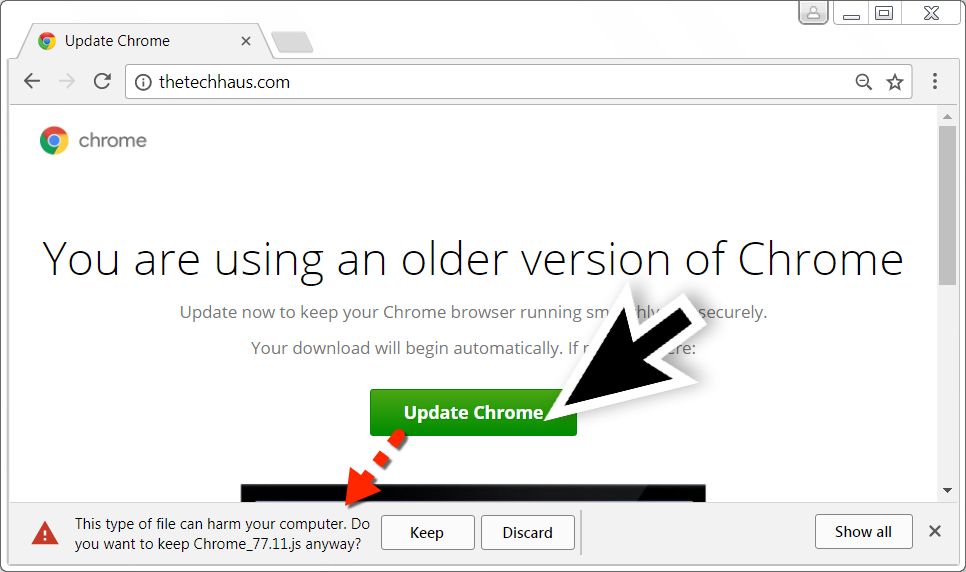
Shown above: You can ignore warnings, download, and run the malicious .js file on a vulnerable Windows host.

Shown above: The .js file shows highly-obfuscated script, which has always been the case for files from this campaign.

Shown above: Start of the infection chain traffic filtered in Wireshark.
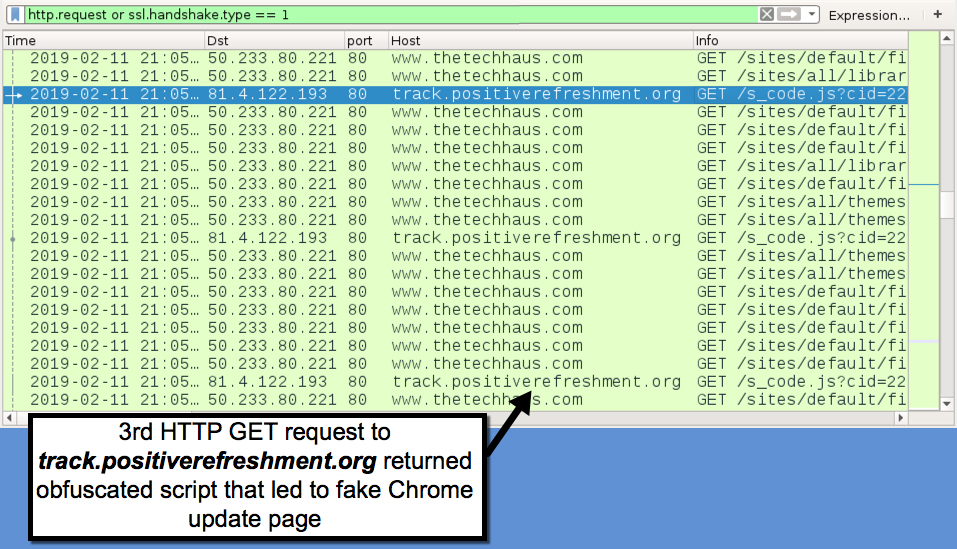
Shown above: Redirect traffic to track.positiverefreshment[.]org that pointed to fake Chrome update page.
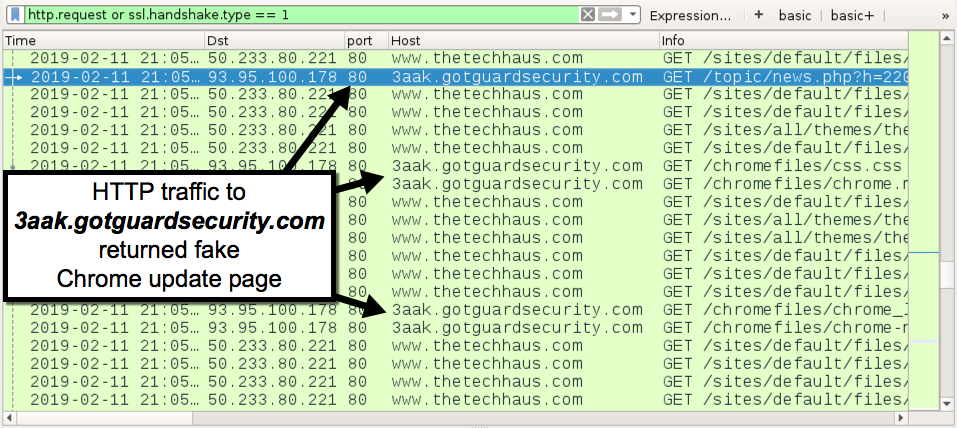
Shown above: Traffic for fake Chrome update page on 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com.
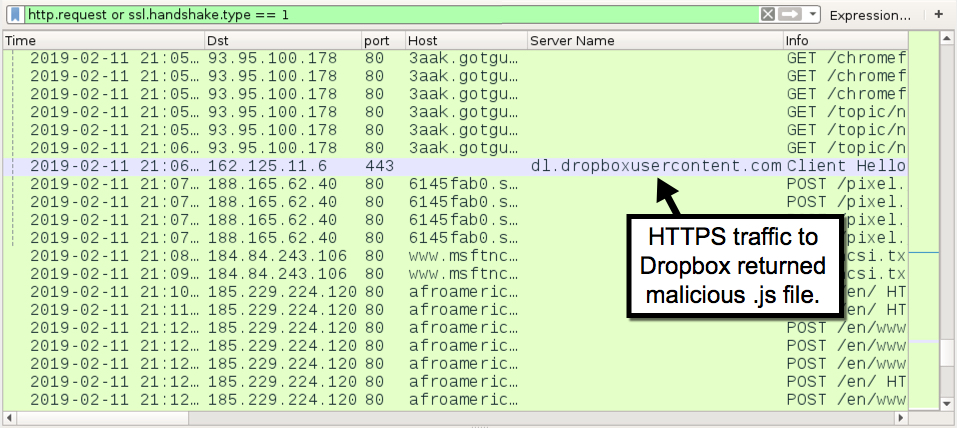
Shown above: HTTPS traffic to dl.dropboxusercontent.com that returned a malicious .js file.
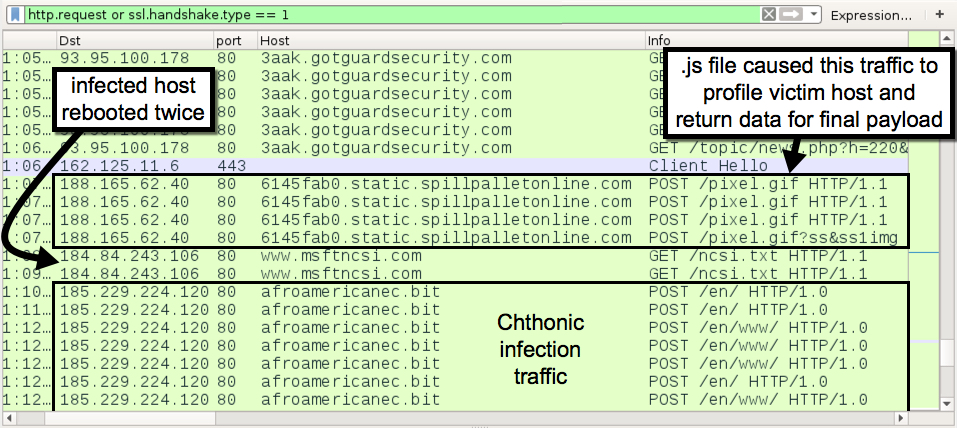
Shown above: Traffic after running the .js file disguised as a Chrome update.
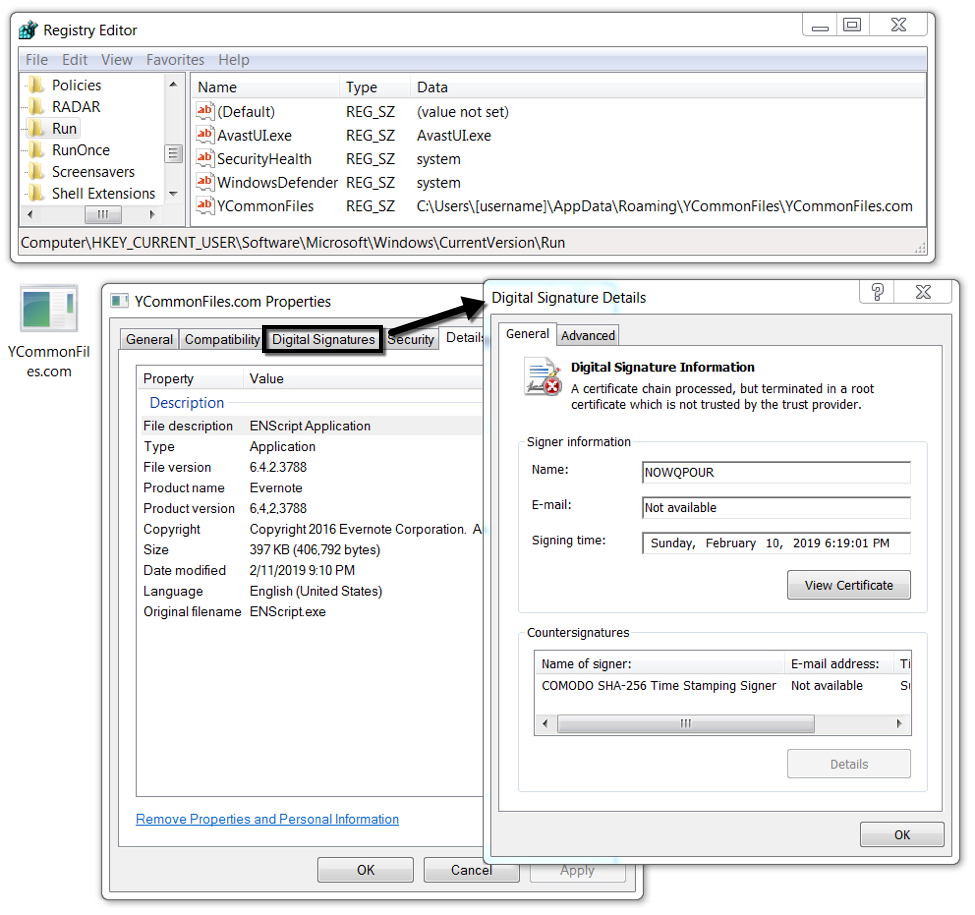
Shown above: Final payload (Chthonic banking Trojan) persistent on the infected Windows host.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
The following are indicators associated with the infection on Monday 2019-02-11.
Initial compromised site:
- thetechhaus[.]com
Redirect that led to fake Chrome update page:
- 81.4.122[.]193 port 80 - track.positiverefreshment[.]org - GET /s_code.js?[3 requests with different strings of characters]
Traffic for fake Chrome update page:
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /topic/news.php?h=220&v=620228&z=de11cb81e3af84d1eb577864be7d7f2d
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /chromefiles/css.css
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /chromefiles/chrome.min.css
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /chromefiles/chrome_logo_2x.png
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /chromefiles/chrome-new.jpg
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /chromefiles/k3k702ZOKiLJc3WVjuplzOgdm0LZdjqr5-oayXSOefg.woff2
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /chromefiles/cJZKeOuBrn4kERxqtaUH3VtXRa8TVwTICgirnJhmVJw.woff2
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /chromefiles/DXI1ORHCpsQm3Vp6mXoaTegdm0LZdjqr5-oayXSOefg.woff2
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /chromefiles/MTP_ySUJH_bn48VBG8sNSugdm0LZdjqr5-oayXSOefg.woff2
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /chromefiles/chrome-32.png
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /topic/news.php?h=220&v=620228&z=de11cb81e3af84d1eb577864be7d7f2d&st=1
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /topic/news.php?h=220&v=620228&z=de11cb81e3af84d1eb577864be7d7f2d&st=2
- 93.95.100[.]178 port 80 - 3aak.gotguardsecurity[.]com - GET /topic/news.php?h=220&v=620228&z=de11cb81e3af84d1eb577864be7d7f2d&st=3
- Note: each time I saw a fake update page, the IP address was the same, but the domain was always different.
Download of .js file disguised as Chrome update:
- port 443 - dl.dropboxusercontent.com - HTTPS traffic
Traffic generated by .js file:
- 188.165.62[.]40 port 80 - 6145fab0.static.spillpalletonline[.]com - POST /pixel.gif
- 188.165.62[.]40 port 80 - 6145fab0.static.spillpalletonline[.]com - POST /pixel.gif?ss&ss1img
- Note: The above domains were also different for each infection.
Post-infection traffic caused by Chthonic banking Trojan:
- [infected lab host restarted twice]
- various IP addresses over TCP port 53 - DNS queries for afroamericanec[.]bit
- 185.229.224[.]120 port 80 - afroamericanec[.]bit - POST /en/
- 185.229.224[.]120 port 80 - afroamericanec[.]bit - POST /en/www/
Associated malware:
SHA256 hash: 9daa0dec909874316afe7f402e82d408b96b215a3501579849c792ec91cfe750
- File size: 41,696 bytes
- File name: Chrome_77.35.js
- File description: malicious .js file returned from dl.dropboxusercontent.com
SHA256 hash: 4a17789f8a03fb2ec3185322ab879d436470d931e1fb98d0a4b9e5b68cda95ab
- File size: 406,792 bytes
- File location: C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Local\Temp\Chrome_77.35.exe
- File description: Second executable dropped to the infected Windows host (Chthonic)
SHA256 hash: 7356424e04f730c7440f76cd822ff8645693b9835ae6aec4d6840cb1becae45c
- File size: 406,792 bytes
- File location: C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Roaming\YCommonFiles\YCommonFiles.com (random names for directory and file name pair)
- File description: Chthonic executable persistent on the infected Windows host.
Final words
Monday's infection was unusual, because everything except for the dropbox URL was regular HTTP traffic. I more often find HTTPS traffic from the compromised site, redirect traffic, and fake update page. Usually the only HTTP traffic is generated by the downloaded .js file and final malware payload.
Pcap and malware samples for today's diary can be found here.
---
Brad Duncan
brad [at] malware-traffic-analysis.net


Comments