When your IoT Device Logs in as Admin, It?s too Late! [Guest Diary]
by Adam Thorman, SANS.edu BACS Student (Version: 1)
[This is a Guest Diary by Adam Thorman, an ISC intern as part of the SANS.edu BACS program]
Introduction
Have you ever installed a new device on your home or company router? Even when setup instructions are straightforward, end users often skip the step that matters most: changing default credentials. The excitement of deploying a new device frequently outweighs the discipline of securing it.
This diary explains a little real-world short story and then walks through my own internship observations overseeing a honeypot and vulnerability assessment that demonstrate just how quickly default credentials are discovered and abused.
Default Credentials in a Real-World Example
Default usernames and passwords remain the most exploited attack vector for Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Whether installation is performed by an end user or a contracted vendor, organizations must have a defined process to ensure credentials are changed immediately. Without that process, compromise is often a matter of when, not if.
During a routine vulnerability assessment at work, I identified multiple IP addresses that were accessible using default credentials. These IPs belonged to a newly installed security system monitoring sensitive material. The situation was worse than expected:
- The system was not placed on the proper VLAN
- Basic end user machines could reach it
- The username “root” remained unchanged and password “password” was changed to “admin”
This configuration was still trivial to guess and exploit, regardless of whether access was internal or external. From my point of view, it was easily guessed and accessed, like Figure 1 below.

Figure 1 - Meme of Easily Bypassed Security Controls
What Logs Showed?
To better understand how common this issue is, I analyzed SSH and Telnet traffic across an eight-day period (January 18–25) and compared it with more recent data. This ties into the story above based on how many devices are kept with their default settings or slightly changed with common trivial combinations. These graphs were pulled from the Internet Storm Center (ISC) My SSH Reports page [2], while the comparison was generated with ChatGPT tool.
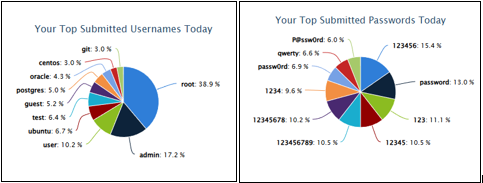
JANUARY 27TH, 2026
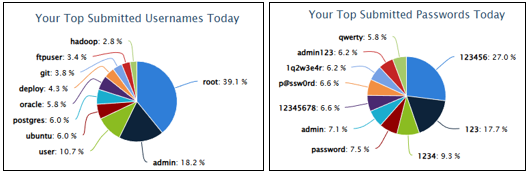
FEBRUARY 17TH, 2026
COMPARISON
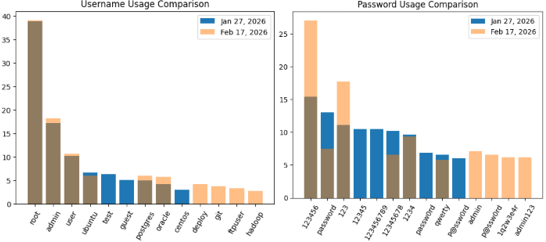
Across both datasets:
- The username “root” remained dominant at ~39%
- The password “123456” increased from 15% to 27%
- These combinations strongly resembled automated botnet scanning behavior
This aligns with publicly known credential lists that attackers use for large scale reconnaissance.
Successful Connections
During the analysis window, I observed:
- 44,269 failed connection attempts
- 1,286 successful logins
- A success rate of only 2.9%
That percentage may appear low, but it still resulted in over a thousand compromised sessions.
To perform this analysis, I parsed Cowrie JSON logs using jq, converted them to CSV files, and consolidated them into a single spreadsheet.
From the 1,286 successful connections:
- 621 used the username root
- 154 used admin as the password
- 406 shared the same HASSH fingerprint 2ec37a7cc8daf20b10e1ad6221061ca5
- 47 sessions matched all three indicators
The matched session to that hash is shown in APPENDIX A.
What Attackers did After Logging in?
Four session IDs stood out during review of the full report:
1. eee64da853a9
2. f62aa78aca0b
3. 308d24ec1d36
4. f0bc9f078bdd
Sessions 1 and 4 focused on reconnaissance, executing commands to gather system details such as CPU, uptime, architecture, and GPU information.
With the use of ChatGPT [3], I was able to compare each session and the commands the attacker attempted to use. It was disclosed that Sessions 1 and 4 had reconnaissance from the topmost digital fingerprint HASSH. They both had the same command but with different timestamps. Refer to APPENDIX B for Session ID 1 and 2 command outputs.
Sessions 2 and 3 demonstrated more advanced behavior:
- SSH key persistence
- Credential manipulation
- Attempts to modify account passwords
Session 308d24ec1d36 ranked as the most severe due to attempted password changes and persistence mechanisms that could have resulted in long term control if it was attempted on a real-world medium. Refer to APPENDIX C for Session ID 2 and 3 command outputs.
Failed Attempts Tell a Bigger Story
Failed authentication attempts revealed even more.
One digital fingerprint alone accounted for 18,846 failed attempts, strongly suggesting botnet driven scanning activity.
On January 19, 2026, there were 14,057 failed attempts in a single day — a significant spike compared to surrounding dates.
From a Security Operations Center (SOC) analyst’s perspective, this level of activity represents a serious exposure risk. It could mean a botnet scanning campaign like the one observed by GreyNoise in late August 2025 [4].
Below is a visual of the top usernames, passwords, and hashes across the analyzed timeframe.
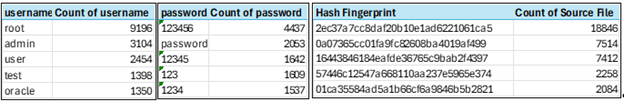
Figure 2 - Top Usernames, Passwords, and Digital Fingerprints
To note in comparison to the other days, where it’s not even half of 14k, Figure 3 below dictates the spread.
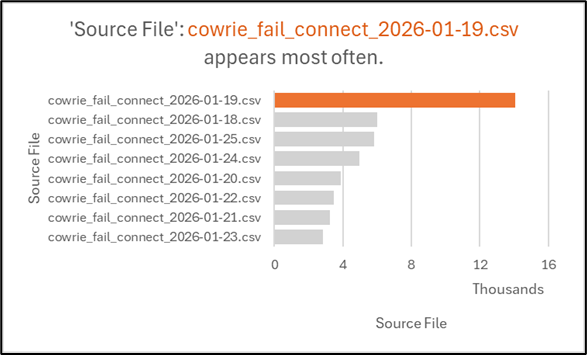
Figure 3 – Failed Connection Attempts Over Time
Best Practices to Follow Towards Resolving Default Credentials
The SANS Cybersecurity Policy Template for Password Construction Standard states that it “applies to all passwords including but not limited to user-level accounts, system-level accounts, web accounts, e-mail accounts, screen saver protection, voicemail, and local router logins.” More specially, the document also states that “strong passwords that are long, the more characters a password has the stronger it is,” and they “recommend a minimum of 16 characters in all work-related passwords [6].”
Establish an immediate policy to change the default password of IoT devices, such an example is a network printer that is shipped with default usernames and passwords [7].
Practical Experience Without the Real-World Disaster
Having access to a controlled sandbox environment, such as a honeypot lab, provides valuable hands-on experience for cybersecurity practitioners.
Sometimes you may need to deal with and see the real-world disaster in a controlled environment to deal with it and see the ripple effect it may produce.
Why Might this Apply to you?
MITRE ATT&CK explicitly documents adversary use of manufacturers set default credentials on control systems. They stress that it must be changed as soon as possible.
This isn’t just an enterprise issue. The same risks apply to:
- Home routers
- Networked cameras
- Printers
- NAS devices
For hiring managers, even job postings that disclose specific infrastructure details can unintentionally assist attackers searching for default credentials.
Ultimately, it’s important to deliberately implement data security measures to protect yourself from data breaches at your home or workplace.
Who Can Gain Valuable Insight on this Information?
Anyone with an internet or digital fingerprint. More specifically, organization leadership and management, when it comes to training your workforce and training your replacements.
A client-tech department, where a team is dedicated to testing the software or devices on the network, to include validating the version of it through a patching management tool, or reference library to know when versions are outdated. Routine “unauthorized” or “prohibited” software reports is an absolute must have in your workplace.
System administrators and SOC analysts are essential to not just know it, but to maintain it. To continue the trend, Cybersecurity students or Professionals such as Red vs. Blue teams [5] for example will gain significant value in this information.
Moving Forward Even with Good Defense
Defense in depth remains critical:
- Strong, unique credentials
- Multi factor authentication where possible [7]
- Device fingerprinting
- Continuous monitoring
SANS also encourage to utilize passphrases, passwords made up of multiple words. [6]
A common saying in Cybersecurity is, “the more secure the data is, the less convenient the data is—the less secure, the more convenient.”
Organizations should also maintain a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) within their cybersecurity program. Even with strong defensive measures, organizations must assume that some security controls may eventually fail. A Business Impact Analysis (BIA) helps organizations prioritize which assets require the strongest protection by identifying critical, operational dependencies, and acceptable downtime thresholds.
Tying it all together. This recommendation to combined with a defense-in-depth strategy, the BIA ensures that the most important systems receive multiple layers of protection such as network segmentation, strong authentication controls, continuous monitoring, and incident response planning. Without this structured approach, organizations may struggle to recover from a compromise or minimize operational disruption.
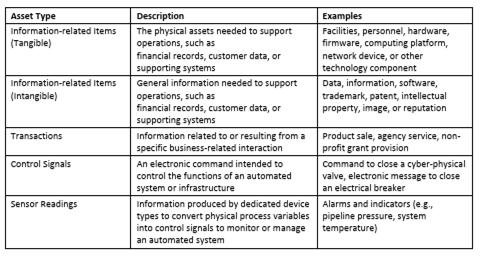
Figure 4 - Examples of Enterprise Business Asset Types [9]
Appendix A - Log Sample
[1] https://www.sans.edu/cyber-security-programs/bachelors-degree/
[2] https://isc.sans.edu/mysshreports/
[3] https://chatgpt.com/
[4] https://eclypsium.com/blog/cisco-asa-scanning-surge-cyberattack/
[5] https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/tip/Red-team-vs-blue-team-vs-purple-team-Whats-the-difference
[6] https://www.sans.org/information-security-policy/password-construction-standard
[7] https://owasp.org/www-project-top-10-infrastructure-security-risks/docs/2024/ISR07_2024-Insecure_Authentication_Methods_and_Default_Credentials
[8] https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T0812/
[9] https://csrc.nist.gov/pubs/ir/8286/d/upd1/final (PDF: Using Business Impact Analysis to Inform Risk Prioritization)
-----------
Guy Bruneau IPSS Inc.
My GitHub Page
Twitter: GuyBruneau
gbruneau at isc dot sans dot edu
Analyzing "Zombie Zip" Files (CVE-2026-0866)
A new vulnerability (CVE-2026-0866) has been published: Zombie Zip.
It's a method to create a malformed ZIP file that will bypass detection by most anti-virus engines.
The malformed ZIP file can not be opened with a ZIP utility, a custom loader is required.
The trick is to change the compression method to STORED while the contend is still DEFLATED: a flag in the ZIP file header states the content is not compressed, while in reality, the content is compressed.
I will show you how to use my tools to analyze such a malformed ZIP file.
Simple Method
Just run my tool search-for-compression.py on the ZIP file (you can download the Zombie ZIP file here, it contains an EICAR file):

The largest compression blob is number 2, it is 77 bytes long. Let's select it:

That's the EICAR file.
Complex Method
We can use the latest version of zipdump.py to analyze the file:
Just using the tool fails (because the zip file is malformed):

Using option -f to bypass the Python ZIP library for parsing, and using custom code to look for ZIP records (-f l) shows us this is a ZIP file, containing a file with the name eicar.com:
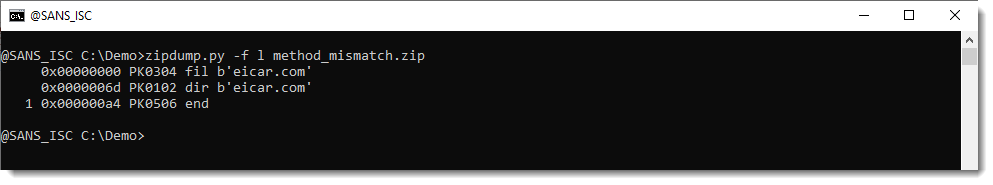
Selecting the FILE record (at position 0x00000000, PK0304 fil) shows us all the meta data:
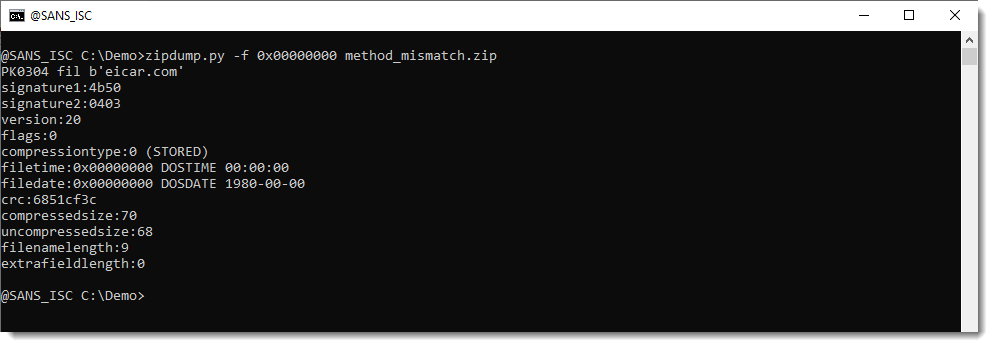
The compressiontype is 0 (STORED), this means that the content of the file is just stored inside the ZIP file, not compressed.
But notice that the compressedsize and uncompressedsize are different (70 and 68). It should be the same for a STORED file.
Let's select the raw file content (-s data) and perform an asciidump (-a):

This does not look like the EICAR file.
Let's force the decompression of the data: -s forcedecompress:

This reveals the EICAR file content.
Option forcedecompress is a new option that I just coded in zipdump.py version 0.0.35. Option decompress will only decompress if the compression type is DEFLATED, thus it can't be used on this malformed ZIP file. Option forcedecompress will always try to decompress (and potentially fail), regardless of the compression type.
Didier Stevens
Senior handler
blog.DidierStevens.com


Comments