Sagan as a Log Normalizer
"Sagan is an open source (GNU/GPLv2) high performance, real-time log analysis & correlation engine that run under *nix operating systems (Linux/FreeBSD/ OpenBSD/etc)."[1]
Sagan is a log analysis engine that uses structure rules with the same basic structure as Snort rules. The alerts can be written to a Snort IDS/IPS database in the Unified2 file format using Barnyard2. This mean the alerts can be read using Sguil, BASE or SQueRT to name a few. It is easy to setup, just need to forward via Syslog the data to a system which has Sagan installed and connected via Barnyard2 to a database (i.e. Sguil). Just follow the Howto documentation to build and install it.
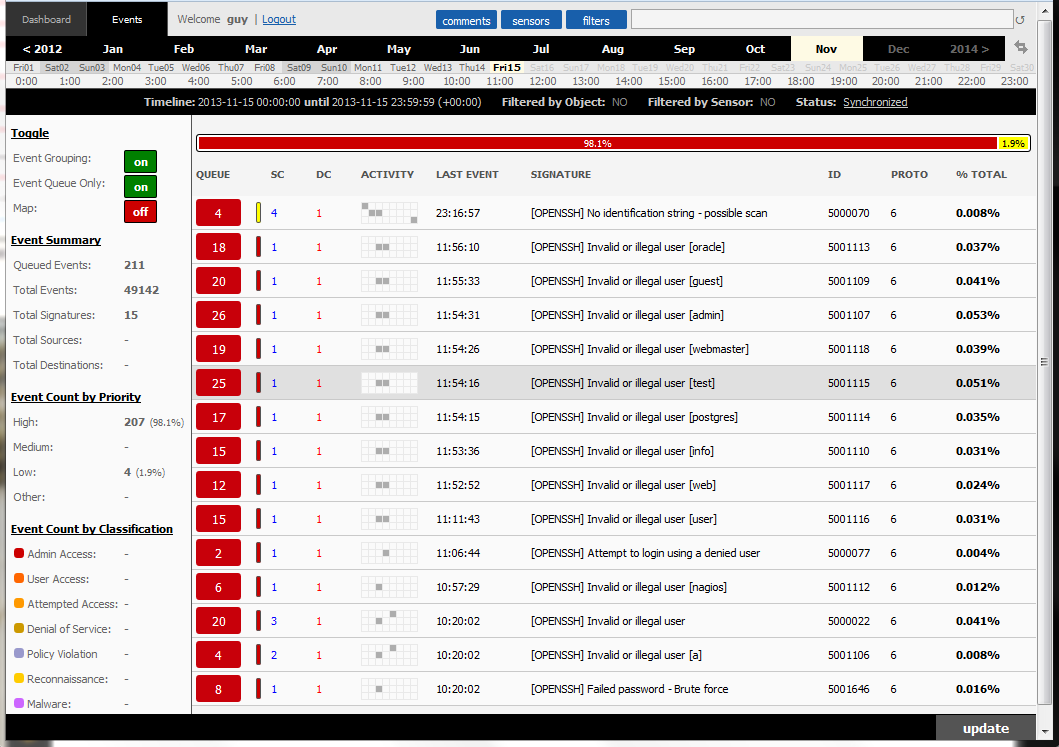
Here is an example of an external gateway monitoring various SSH account breaking attempts being logged by Sagan rules and the alerts sent to a Sguil database.
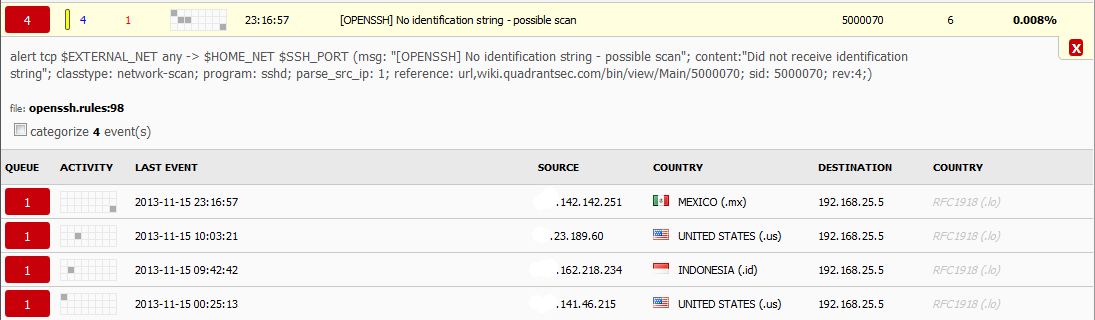
Expanding the first event "[OPENSSH] No identification string - possible scan", you can now view (in SQueRT) the rule that trigger these events and a summary of the events by the time it happened, the source and the target.
In order to further examine this activity, l need to login in Sguil and search the IP of the first event (xxx.142.142.251) using sancp as a source address to find if any other related activity has been recorded from this source. The sancp log shows that 2 separate connection were made to access SSH which access is restricted to a number of addresses.
Using Sagan is another way of leveraging a Snort IDS database infrastructure to collect, correlated and monitor suspicious events via syslog. For additional information on Sagan, check the Sagan Wiki.
[1] http://sagan.quadrantsec.com/
[2] https://wiki.quadrantsec.com/twiki/bin/view/Main/SaganMain
[3] https://wiki.quadrantsec.com/twiki/bin/view/Main/SaganRuleReference
[4] https://wiki.quadrantsec.com/twiki/bin/view/Main/SaganInstall
[5] http://sagan.quadrantsec.com/rules/
[6] https://github.com/beave/sagan
-----------
Guy Bruneau IPSS Inc. gbruneau at isc dot sans dot edu



Comments