My Little CVE Bot
The massive spread of the WannaCry ransomware last Friday was another good proof that many organisations still fail to patch their systems. Everybody admits that patching is a boring task. They are many constraints that make this process very difficult to implement and... apply! That’s why any help is welcome to know what to patch and when. This is the key:
- What to patch? What are the applications/appliances that are deployed in your infrastructure?
- When to patch? When are new vulnerabilities discovered?
The classification of vulnerabilities is based on the “CVE” (or “Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures”) standard maintained by mitre.org[1]. To explain briefly, when a security researcher or a security firm finds a new vulnerability, a CVE number is assigned to it (CVE-YYYY-NNNNN). The CVE contains all the details of the vulnerability (which application/system is affected, the severity and many more information). As an example, the vulnerability exploited by WannaCry was CVE-2017-0143.
Those CVE are stored in open databases and many organisations are using them and provide online services like cvedetails.com[2]. There are plenty of them that offer almost all the same features but they don't really match my requirements. My favourite tool to search for CVE is the cve-search project[3]. Why? Because you can have the complete CVE database with you (read: offline) and you can search using command line tools. Note a web interface is also available:
.png)
Based on cve-search, I can provide details about new CVE's to my customers or any other organisations just by querying the database. Indeed, reading the daily flow of CVE is difficult and useless for many people. They have to focus on what affect them. To help them, I'm using a quick & dirty shell script that parses a simple config file like this:
$ cat cve-tracker.conf [email protected]|1|csv|microsoft:windows_10|pfsense [email protected]|5|json|apple:iphone_os [email protected]|1|html|cisco:ios:12.4|cisco:aironet_1850i
The format is easy: one customer per line
<email_contact> | <days_to_check> | <output_format> | <product_definition> [ | <product_definition> ] ...
The script will parse this config file and search for new CVE for each product definition. Results will be sent via email to the specified address.
As I’m using CVE-Search in a docker[4], I scheduled a crontab:
0 6 * * * docker exec -i cvesearch /opt/cve-search/bin/cve-tracker.sh
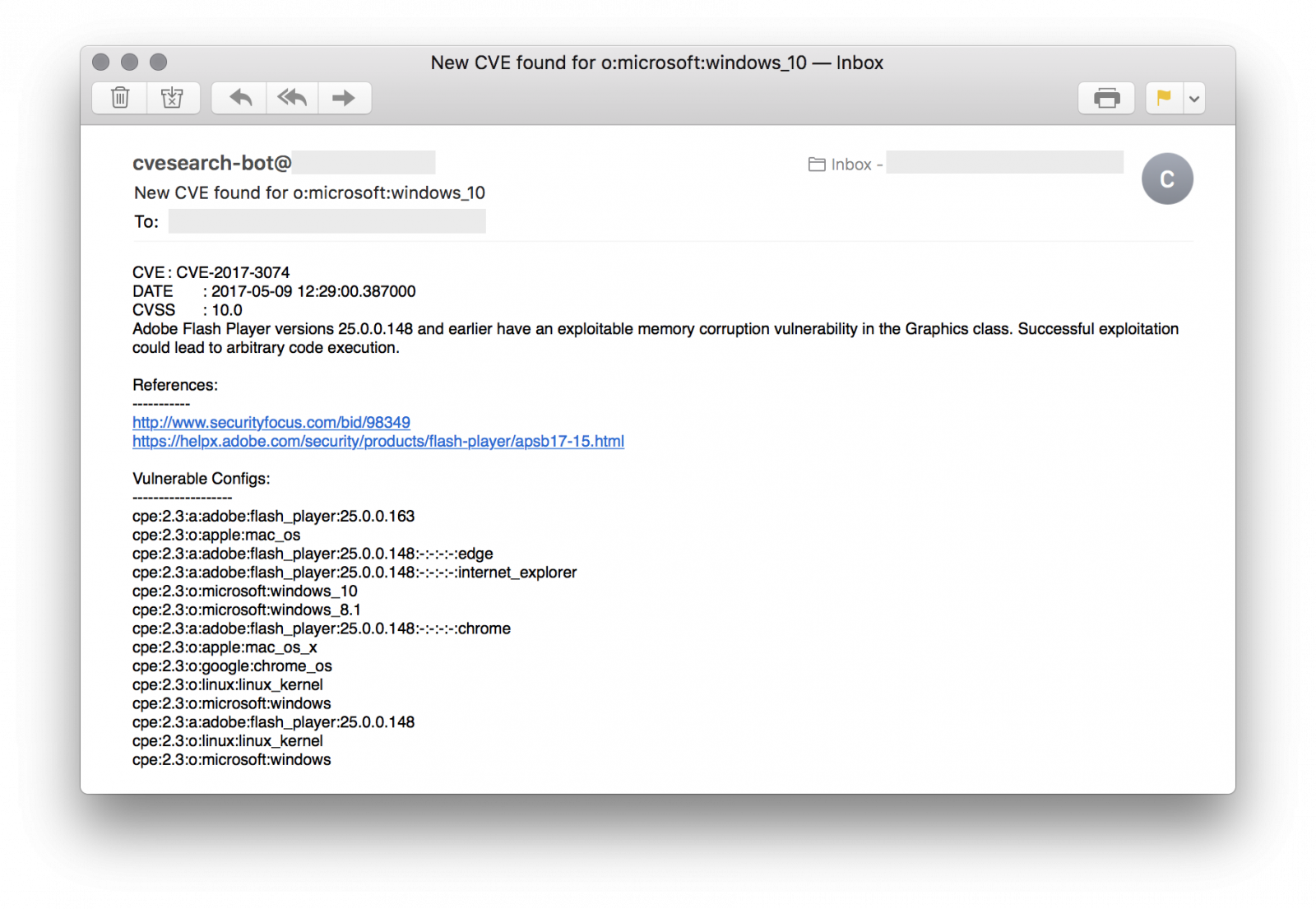
Of course, the main requirement is to know what you are using on your infrastructure. The information used in the config file describes the products is based on the CPE standard[6] which categorises applications, operating systems and hardware devices. This information can be found by Nmap. An alternative is to use the following tool on your own network (only!): cve-scan[7]. It scans hosts and searches for vulnerabilities in the cve-search database.
My script is available on my GitHubrepository[5].
[1] https://cve.mitre.org
[2] http://www.cvedetails.com/
[3] https://github.com/cve-search/cve-search
[4] https://hub.docker.com/r/rootshell/cvesearch/
[5] https://github.com/xme/toolbox
[6] http://cpe.mitre.org/
[7] https://github.com/NorthernSec/cve-scan
Xavier Mertens (@xme)
ISC Handler - Freelance Security Consultant
PGP Key


Comments